[JAVA] Hash
List와 Set
List
요소들의 순차적인 컬렉션, 특정 순서를 가지고 중복을 허용한다.
- 순서 유지 → 특정 순서를 유지한다 이 순서는 요소가 추가된 순서를 반영할 수 있다.
- 중복 허용 → 동일한 값이나 객체의 중복을 허용
- 인덱스 접근 → 리스트의 각 요소는 인덱스를 통해 접근할 수 있다. 보통 0부터 시작한다.
1
2
3
4
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("사과");
list.add("사과"); // 중복 허용
System.out.println(list); // [사과, 사과]
Set
유일은 요소들의 컬렉션, 중복을 허용하지 않고 요소의 유무만 중요한 경우에 사용
- 유일성 → 중복된 요소가 존재하지 않는다. 이미 존재하는 요소면 무시된다.
- 순서 미보장 → 요소를 출력할때 입력 순서와 다를 수 있다.
- 빠른 검색 → 빠르게 확인할 수 있게 최적화 되어 있어 빠른 조회 가능
1
2
3
4
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("사과");
set.add("사과"); // 중복무시
System.out.println(set); // [사과]
List → 장바구니에 같은 상품을 여러번 담을 수 있다.
Set → 응모자 중복을 제거하여 한 번만 응모가 가능하게 하는 경우.
Set 직접구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public class MyHashSetV0 {
//배열 크기 10 고정
private int[] elementData = new int[10];
private int size = 0;
// O(n)
public boolean add(int value) {
//셋에 중복된 값이 있는지 체크
if(contains(value)) {
return false; //중복값 있으면 false 반환
}
//중복값 없으면 저장 후 true 반환
elementData[size++] = value;
return true;
}
// O(n)
public boolean contains(int value) {
//셋에 값이 있는지 확인
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if(elementData[i] == value) {
return true; //있으면 true
}
}
return false;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyHashSetV0{" +
"elementData=" + Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size)) +
", size=" + size +
'}';
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class MyHashSetV0Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHashSetV0 set = new MyHashSetV0();
set.add(1); //O(1)
set.add(2); //O(n)
set.add(3); //O(n)
set.add(4); //O(n)
set.add(5); //O(n)
System.out.println(set);
boolean result = set.add(4);//중복 데이터 저장
System.out.println("중복 데이터 저장 결과 " +result);
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println("set.contains(3) = " + set.contains(3)); //O(n)
System.out.println("set.contains(99) = " + set.contains(99)); //O(n)
}
}
//실행결과
MyHashSetV0{elementData=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], size=5}
중복 데이터 저장 결과 false
MyHashSetV0{elementData=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], size=5}
set.contains(3) = true
set.contains(99) = false
add()로 데이터를 추가할때 중복 데이터가 있는지 전체 데이터를 항상 확인해 성능이 좋지 않다.O(n)contains()로 데이터 찾을때 배열의 모든 데이터를 찾고 비교해야 하므로 성능이 좋지 않다.O(n)
결국 중복 데이터를 찾는 부분때문에 성능이 좋지 않다. 이 부분을 개선해보자
Hash Algorithm
해시 알고리즘을 사용해 검색 성능을 평균 O(1) 로 높일 수 있다.
index 사용
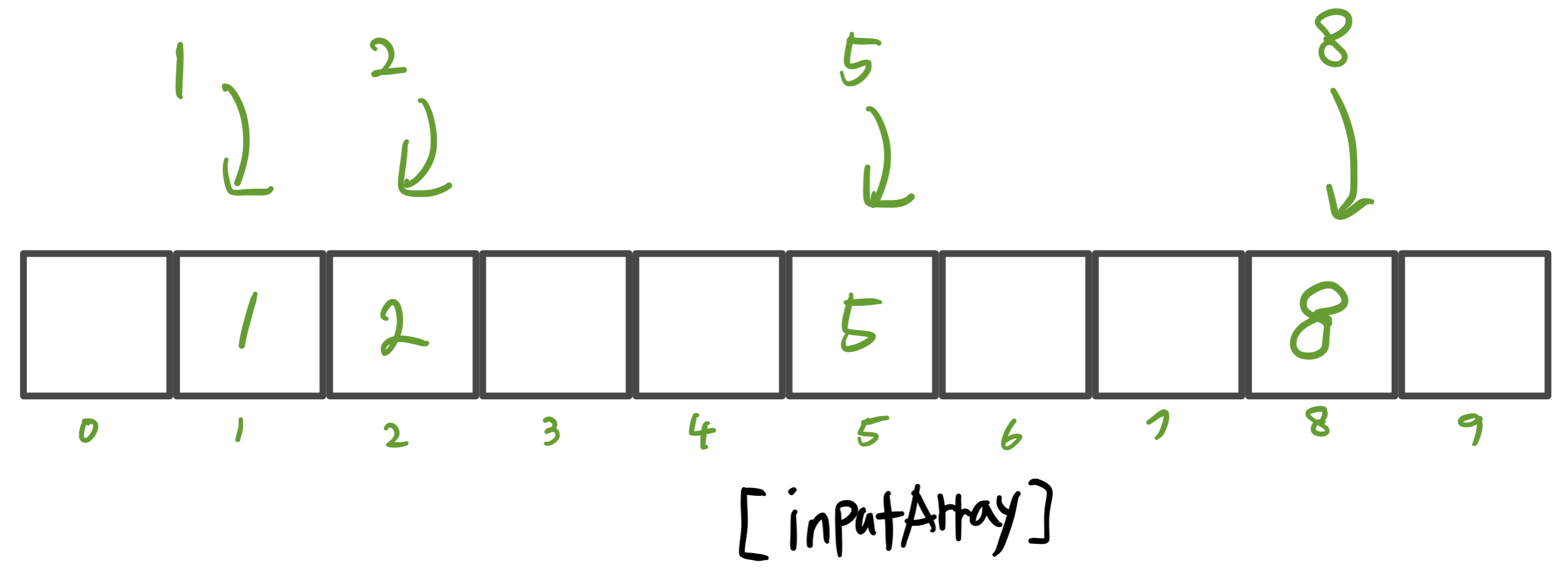
배열의 인덱스의 위치를 사용해서 데이터를 찾을 때 O(1)로 매우 빠르다. 하지만 검색기능은 인덱스와 데이터 값이 서로 다르기 때문에 불가능하다. 하지만 데이터의 값 자체를 배열의 인덱스로 사용하면 어떻게 될까?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] inputArray = new Integer[10];
inputArray[1] = 1;
inputArray[2] = 2;
inputArray[5] = 5;
inputArray[8] = 8;
System.out.println("inputArray[] = " + Arrays.toString(inputArray));
int searchValue = 8;
Integer result = inputArray[searchValue];
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
//실행결과
inputArray[] = [null, 1, 2, null, null, 5, null, null, 8, null]
searchValue = 8
- 배열에서 인덱스로 값을 찾는건 빠르다
O(1)
메모리 낭비
만약 입력값의 범위를 int 숫자의 모든 범위로 입력하면 42억 사이즈의 배열이 필요하다. 따라서 데이터의 값을 인덱스로 사용하는 방법은 빠른 성능을 보장하지만 입력 값의 범위가 커지면 메모리 낭비가 심해진다.
나머지 연산
공간도 절약하고, 넓은 범위의 값을 사용할 수 있는 나머지 연산을 이용해보자 배열의 크기를 10이라 가정하고 그 크기에 맞춰 나머지 연산을 사용하면 된다.
1, 2, 5, 8, 14, 99의 값을 크기가 10인 배열에 저장해보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
public class HashStart4 {
static final int CAPACITY = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//{1,2,5,8,14,99}
System.out.println("hashIndex(1) = " + hashindex(1));
System.out.println("hashIndex(2) = " + hashindex(2));
System.out.println("hashIndex(5) = " + hashindex(5));
System.out.println("hashIndex(8) = " + hashindex(8));
System.out.println("hashIndex(14) = " + hashindex(14));
System.out.println("hashIndex(99) = " + hashindex(99));
Integer[] inputArray = new Integer[CAPACITY]; //크기 10
add(inputArray, 1);
add(inputArray, 2);
add(inputArray, 5);
add(inputArray, 8);
add(inputArray, 14);
add(inputArray, 99);
System.out.println("inputArray = " + Arrays.toString(inputArray));
//검색
int searchValue = 14;
//hashIndex를 구한 후 그 위치에 데이터 저장
int hashIndex = hashindex(searchValue);
System.out.println("searchValue hashIndex= " + hashIndex);
Integer result = inputArray[hashIndex]; //O(1)
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
private static void add(Integer[] inputArray, int value) {
int hashIndex = hashindex(value); //hashIndex를 먼저 구한 후
inputArray[hashIndex] = value; //값을 넣음
}
//hashIndex를 반환
static int hashindex(int value) {
return value % CAPACITY;
}
}
//출력결과
hashIndex(1) = 1
hashIndex(2) = 2
hashIndex(5) = 5
hashIndex(8) = 8
hashIndex(14) = 4
hashIndex(99) = 9
inputArray = [null, 1, 2, null, 14, 5, null, null, 8, 99]
searchValue hashIndex= 4
result = 14
- 해시 인덱스를 사용해
O(1)의 성능으로 데이터를 저장,조회할 수 있게 되었다.
해시 충돌과 저장
다른 값을 입력했지만 같은 해시 코드가 나오게 되는 경우
99 % 10 = 9
9 % 10 = 9
해시 충돌이 발생하면 마지막에 저장한 값 9만 남게 된다. 입력값을 늘리면 충돌이 발생하지 않지만 메모리 낭비가 심해진다. 그리고 모든 int 숫자를 다 받는 문제를 해결할 수 없다. 어떻게 해결할 수 있을까?
해시 충돌 해결
해시 충돌이 일어났을 때 같은 해시 인덱스의 값을 같은 인덱스에 함께 저장해버린다.
즉 배열 안에 배열을 만들면 된다.
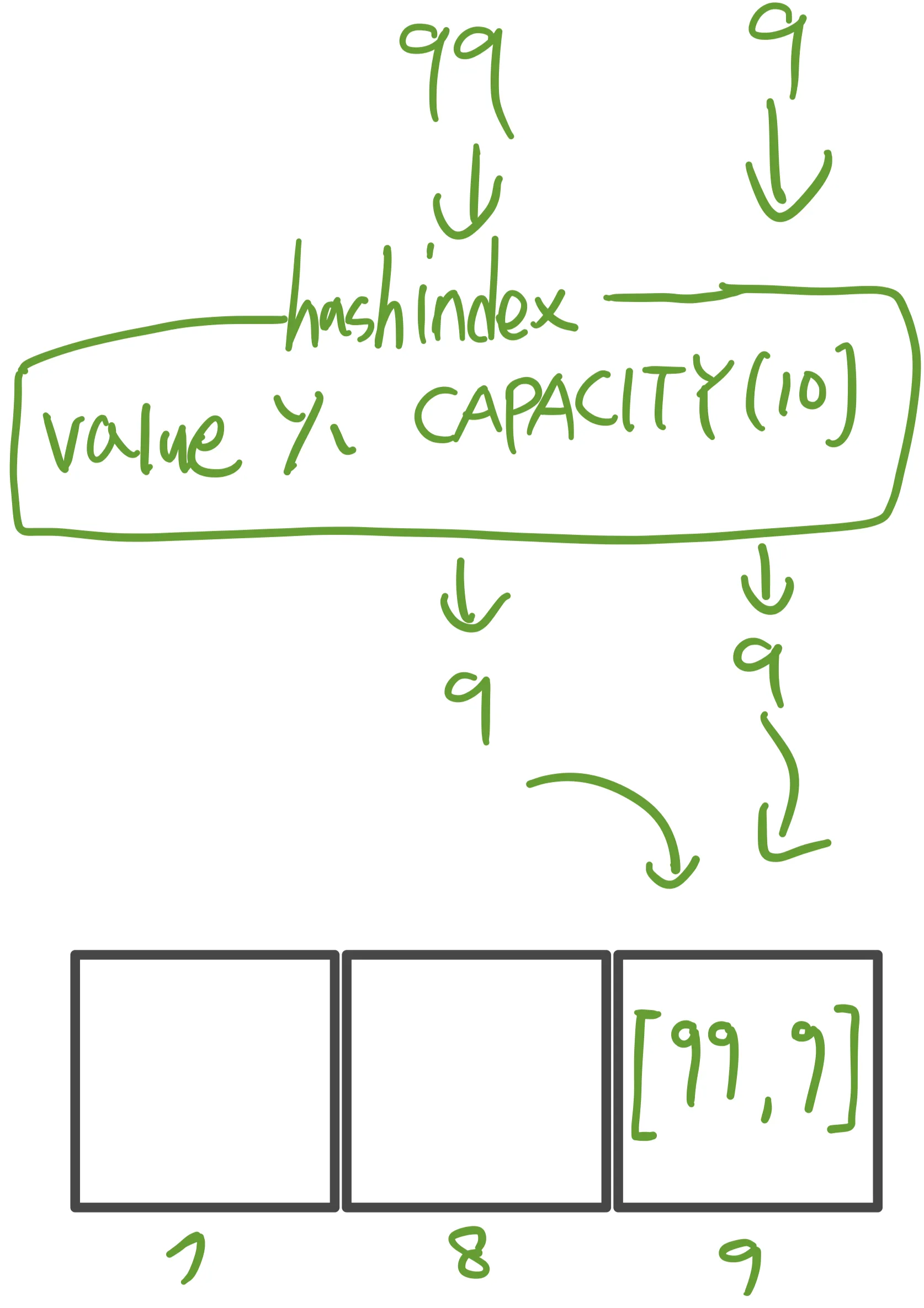
99를 조회한다 가정하면
- 99의 해시 인덱스 → 9
- 배열에서 9번 인덱스를 찾음
- 배열 안에는 또 배열이 있다. 여기서 모든 값을 검색할 값과 하나씩 비교
- [99, 9]의 데이터에서 99를 찾는다. 1번째에 원하는 데이터를 찾는다!
최악의 경우
9, 19, 29, 99의 해시 인덱스는 모두 9 따라서 9번 인덱스에 모든 데이터가 저장된다.
최악의 경우 O(n) 의 성능을 보이지만 확률적으로 넓게 퍼지기 때문에 대부분 O(1)의 성능을 제공한다. 해시 충돌이 가끔 발생한다 해도 내부에서 값을 몇 번 비교하는 수준이라 대부분 빠르게 값을 찾을 수 있다.
해시 충돌 구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
public class HashStart5 {
static final int CAPACITY = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//LinkedList가 들어가는 배열
LinkedList<Integer>[] buckets = new LinkedList[CAPACITY];
//각 인덱스에 new LinkedList<>()를 넣어 초기화
for(int i = 0; i < CAPACITY; i++) {
buckets[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
add(buckets, 1);
add(buckets, 2);
add(buckets, 5);
add(buckets, 8);
add(buckets, 14);
add(buckets, 99);
add(buckets, 9); //중복
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buckets));
//검색
int searchValue = 9;
boolean contains = contains(buckets, searchValue);
System.out.println("buckets.contains("+searchValue+") = " + contains);
}
//데이터 등록
private static void add(LinkedList<Integer>[] buckets, int value) {
int hashIndex = hashIndex(value); //해시 인덱스 구하기
//해시 인덱스로 배열의 인덱스 찾기
LinkedList<Integer> bucket = buckets[hashIndex]; //O(1)
if(!bucket.contains(value)) { //중복체크 //O(n)
bucket.add(value);
}
}
private static boolean contains(LinkedList<Integer>[] buckets, int value) {
int hashIndex = hashIndex(value); //해시 인덱스 구하기
LinkedList<Integer> bucket = buckets[hashIndex]; //[99, 9] 나옴
return bucket.contains(value); //contains = 루프 자동으로 돌아줌 true/false
}
public static int hashIndex(int value) {
return value % CAPACITY;
}
}
1
2
//배열 선언
LinkedList<Integer>[] buckets = new LinkedList[CAPACITY];
- 해시 충돌을 고려해 배열 안에 연결 리스트(LinkedList)가 들어간다, 연결 리스트 안에 데이터가 들어있는 구조
Add 순서
- 해시 인덱스 구하기
1
int hashIndex = hashIndex(9); // → 9 % 10 = 9
- 해당 buckets 선택
1
LinkedList<Integer> bucket = buckets[9]; // 9번 바구니
- 중복체크
1
2
3
if (!bucket.contains(9)) {
...
}
contains()는LinkedList내부 요소를 순회하며equals()비교 →O(n)
- 데이터 추가
1
bucket.add(9); // 중복 없을 경우만
정리
List는 순서와 중복이 중요한 경우 사용Set은 중복을 제거하고, 빠른 검색이 필요한 경우 사용- 해시는 검색 속도를 극적으로 개선하지만, 충돌 해결 구조도 필요
- 실무에선
HashSet,LinkedHashSet,TreeSet등 목적에 따라 사용